The Next Generation of Low Dead Space Disposable Syringes
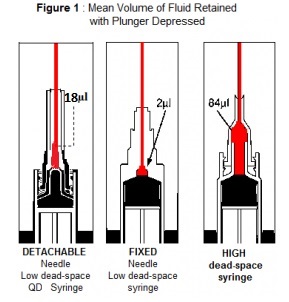
Excess waste is a well-known known driver of inefficiency in the US health care system. Medication waste contributes to this inefficiency and has recently been described among cancer medications, but it may also be attributable to the syringes used to deliver injectable medications. Syringe dead space is the volume of residual fluid that remains within the syringe after the plunger is fully depressed during medication injection. High dead space syringes, compared with low dead space syringes, are associated with increased risk for medication waste. If costly injectable medications are administered using high dead-space syringes, syringe dead space may contribute to excess medication waste in the US health care system. We estimated differences in the cost of injectable medication waste attributable to high dead space syringes and low dead-space syringes.
A new study finds that high dead-space syringes, characterized by a detachable needle, are especially wasteful. Researchers determined that the median cost of wastage for self-injectable drugs delivered through high dead space syringes was $5.43 per single dose and $1,637.91 annually. By comparison, wastage from medication dispensed through low dead-space syringes was significantly less at a median $0.54 and $124.52, respectively. Replacing high dead space syringes with low dead space syringes, which have a permanently attached or integrated needle and/or a conical plunger to shrink dead space in the needle hub, is seen a one way to avoid preventable medication waste.
Written by:
Tags: glyflo, glyflo technology, high dead space syringes, low dead space syringes, low residual volume syringes, low waste syringes, qd syringe
Views: 620
© 2026 Created by Christopher Green.
Powered by
![]()